Exploring Narrow Therapeutic Index Drugs

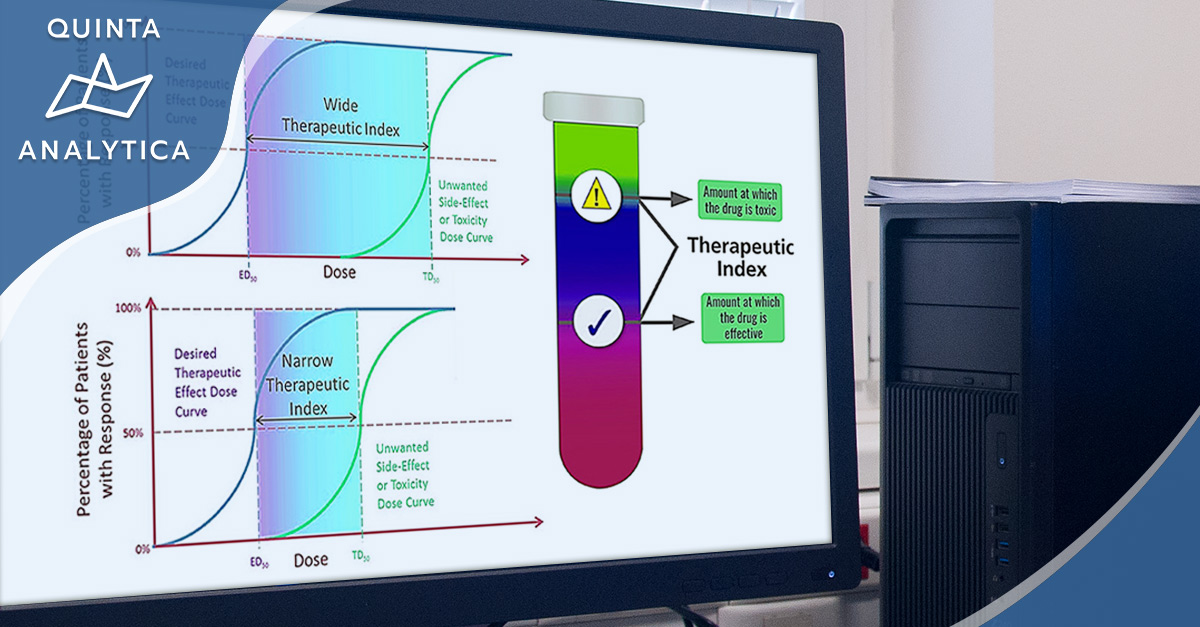
Narrow therapeutic index (NTI) drugs are defined as those drugs where small differences in dose, or concentration in the blood, may lead to serious therapeutic failures or adverse drug reactions.
Such is the precision in this narrow administration window, get it wrong and there is the very real possibility of serious events including those which are persistent, slowly reversible, irreversible, or even life-threatening.
There are very few scenarios where a Bioequivalence assessment is more important than in the testing of these types of drugs. To mitigate that, the bioequivalence assessment has its specific acceptance interval for AUC tightened to 90.00-111.11%, compared to the regular 80.00-125-00% interval required by bioequivalence guidelines.
Where Cmax is of particular importance for safety, efficacy, or drug level monitoring the 90.00-111.11% acceptance interval applies for this parameter too.
Given the above, it’s safe to say that getting the design of the clinical studies right for this undertaking is critical. In addition to carefully chosen doses that are safe for volunteers, there is extremely close monitoring of their wellbeing ranging from frequent physical examinations to laboratory parameter controls with enhanced supervision by medical staff.
With no margin for error in this type of testing, choosing a highly experienced partner such as QUINTA-ANALYTICA is commensurate with success. With decades of clinical and bioanalytical experience with NTI drugs, such as levothyroxine, hydroxyurea, anagrelide, torasemide, ticagrelor, and many more, they bring world-class knowledge and first-class experience in this key area, and instill professionalism and confidence into the whole process.
Get in touch with the Quinta team for a no-obligation discussion.




